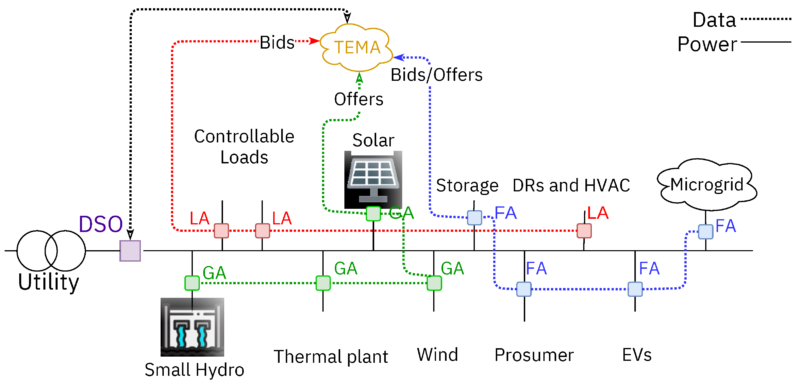
AITU staff, in collaboration with scientists from Turkey (Gazi University) and the UK (The University of Edinburgh), published an article in the rating journal “Energies” and with Impact Factor: 3.004. In the article, a new effective way to control electricity in a microgrid is investigated and proposed by modeling methods. The task is complicated by the fact that the system has agents representing unstable renewable energy sources, battery stations, electric vehicles and consumers. The article formulates the shortcomings of existing methods and proposes a new framework for the optimal integration of Transactive Energy into a smart grid and includes an auction algorithm. The system is modeled as a virtual power plant based on a day-ahead market and a balancing market between agents that regulate system profits and energy imbalances.
The results of the study showed that auction markets can be used for optimal scheduling, as well as for managing congestion and minimizing system costs. A method for reducing congestion is proposed that takes into account incentives for key agents participating in a transactive energy network. The results of the study show that the multi-agent approach allows the owners of energy resources to form and participate in local energy markets.
This international study (Kazakhstan, Turkey, UK) was funded by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan (grant AP09261258) and the authors acknowledge the Scolarship Programme from Islamic Development Bank and the programme of Royal Academy of Engineering for developing an academic netwroks.
You can read more in the open access article:
Amanbek, Y., Kalakova, A., Zhakiyeva, S., Kayisli, K., Zhakiyev, N., & Friedrich, D. (2022). Distribution Locational Marginal Price Based Transactive Energy Management in Distribution Systems with Smart Prosumers—A Multi-Agent Approach. Energies, 15(7), 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072404 ISSN: 1996-1073