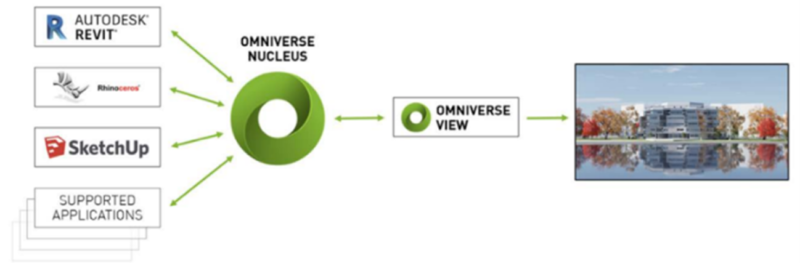
NVIDIA Omniverse is an open, cloud-based platform that accelerates design and simulation workflows and collaborates in real time on photorealistic quality designs. Omniverse empowers designers, engineers, and researchers to collaborate in virtual worlds in which they are connected. The platform provides designers and developers with “portals” that connect their working environments in live mode, for example, Autodesk Maya, Adobe Photoshop and Unreal Engine. Using Omniverse, each team member can see all the changes made by others without noticeable delay. The platform increases efficiency, productivity, and flexibility as teams from the same room and anywhere in the world can log into Omniverse and collaborate on projects with real-time photorealistic rendering.
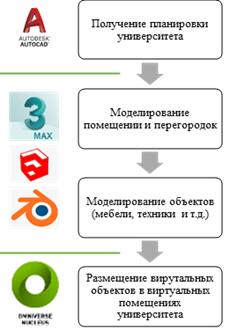
A key feature of Omniverse is the ability to easily work in different software at the same time. Content creators, designers, and engineers have access to industry-leading applications such as Autodesk Maya and Revit, Adobe Photoshop, Substance Designer, Substance Painter, McNeel Rhino, Trimble SketchUp and Epic Unreal Engine, Autodesk 3ds Max. Many more are in development, including Blender, SideFX Houdini, and AutoDesk MotionBuilder.
The platform uses Pixar’s open Universal Scene Description (USD) technology to share information about models, animations, visual effects, and rendering. In addition, it supports the Material Definition Language (MDL), a language for transferring data about object materials, developed by NVIDIA.